The benefits of BCAAs in Bodybuilding

amino acids are the building blocks of muscle protein . Getting adequate amounts of amino acids is difficult for those who exercise. Exercise burns amino acids quickly. Failure to replenish the body with adequate amino acids can make hard working people almost no progress. That is why the importance of taking a BCAA.
supplement
Amino acids are most used in free and branched chain form. These amino acids do not require digestion and enter directly into the bloodstream for immediate use by muscle cells. BCAAs also provide 70% of the body’s nitrogen needs.
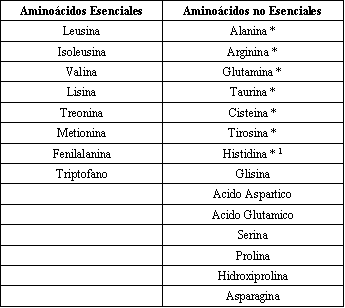
What is the difference between essential amino acids (BCCA) and non-essential amino acids?
Essential amino acids cannot be produced by the body. You should get them from whole protein-rich foods or a combination of plant-based foods.
Non-essential amino acids are synthesized (manufactured) by the body itself from other existing amino acids. They can be produced on their own from vitamins and other amino acids.

The term “non-essential” can be misleading as all amino acids are essential for metabolism and some non-essential, such as glutamine, can become very essential in the event of illness or trauma.
The essential fatty acids of branched chain (BCAA) are of special importance to athletes because they are metabolized in the muscle, rather than in the liver. Here’s how it works: After protein is digested, they are broken down into individual amino acids, these amino acids can be used to build new proteins or be burned as fuel for energy.
The BCAAs in bodybuilding
Bodybuilders who want to avoid losing muscle size and strength will find BCAA supplements very useful . Keep in mind that an adequate level of BCAAs will not make you Superman, but it will allow you to avoid some of the negative effects of BCAA depletion, including poor recovery and stagnant training.
If you already have an adequate level provided by your diet, you are really going to be able to see the benefits. In addition to getting enough protein to eat, make sure you’re getting enough quality calories on a daily basis and getting plenty of rest and recovery. Consuming adequate amounts of calories and carbohydrates will help you preserve BCAAs.
The higher the glycogen storage, the more likely BCAAs are used for muscle growth and the less likely they are to be oxidized for energy. Rest and recovery directly help BCAA storage for muscle growth.
5 benefits of BCAAs
Now is the time for good things What can BCAA supplements do for you? Science has shown us that BCAA supplementation can have positive effects on the body. These effects include:
1. Increased recovery
Perhaps the greatest benefit for athletes who train hard is the increased metabolic recovery that follows supplementation. Most athletes experience a decrease in muscle soreness after exercise with BCAA supplementation. This means faster recovery from exercise-induced protein damage (remember, your muscles grow when they are damaged), which in turn means greater size and strength. With a greater recovery you will be able to reach your goals more quickly.
2. Improved resistance
BCAAs can serve as a nitrogen donor in the formation of L-alanine, which provides the body with glucose after glycogen stores have been depleted.
BCAA supplementation allows you to maintain the intensity of your training, the endurance and the energy that is normally lost by a decrease in your diet. Anyone who has been on a very low-carb or low-calorie diet for extended periods of time can certainly appreciate this.
3. Stimulates protein synthesis
BCAAs by themselves have been shown to stimulate muscle protein synthesis independently. In other words, they have shown the ability to induce muscle mass gains, even in the absence of weight training.
Studies have shown that BCAA supplementation increases hormones: testosterone, growth hormone and insulin .
4. Stimulate fat loss
Supplementation of BCAAs has been shown to activate significant losses of body fat in the viscera. Located in the deeper layers of the body and in the subcutaneous fat, visceral fat tends to be resistant to diet and is difficult to lose. In a study conducted, 25 bodybuilders were divided into 3 groups: a diet high in BCAA , a diet low in BCAA and a controlled diet. The bodybuilders maintained the diet for a month. The results showed that those on a high BCAA diet lost more fat than the others.

When present in large amounts during exercise, the body detects these high levels of BCAAs in the blood which is usually a sign of excessive muscle breakdown. So the body stops wearing down the muscle and uses more fat for fuel. At the same time, the extra BCAAs in the blood stimulate insulin so that the BCAAs are delivered directly to the muscle.
How much BCAA should I take?
Dosages for those who exercise are 5 grams of leucine, 4 grams of valine, and 2 grams of isoleucine per day to prevent muscle loss and increase muscle gain.
Leave a Reply